Table of Contents
Lab #1 - SystemVerilog and Vivado Review
In this lab you will refresh your understanding of the Vivado tools used in ECEN 423, learn about the ECEN 423 lab submission process, and review your SystemVerilog RTL coding skills that you learned in ECEN 320/220. You will demonstrate your SystemVerilog skills by downloading a circuit on the Basys3 FPGA board used in ECEN 320/220 (access to a board is required for this and most labs in this class). Much of this laboratory assignment will be a review and the amount of time you spend on this lab will depend on your familiarity with Unix, GitHub, the Vivado tools, and SystemVerilog RTL.
We track the amount of time students take to complete labs to help us understand the lab difficulty. The time taken by students in this lab when taught as ECEN 423 in Winter of 2026 is shown below. Such graphs will give you an idea on the complexity of the lab and help you plan your time accordingly.
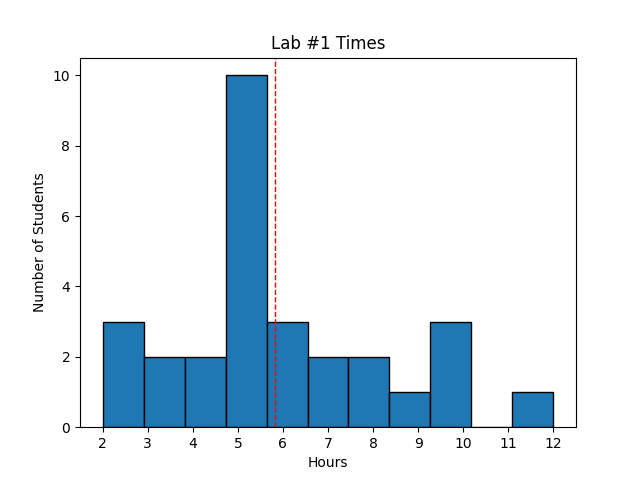 Avg Hours: 5.8, 4.6, 4.7, 4.8, 3.6 (Winter 2026, 2024, 2023, 2022, 2021)
Avg Hours: 5.8, 4.6, 4.7, 4.8, 3.6 (Winter 2026, 2024, 2023, 2022, 2021)
Learning Outcomes
- Understand how to complete and submit lab reports
- Review how to simulate, synthesize, and generate bitstream files from a SystemVerilog file
- Review your SystemVerilog design skills by modifying an existing SystemVerilog file
- Review your understanding of the Vivado design tools by simulating your SystemVerilog module
- Learn how to download your SystemVerilog module onto the Basys3 FPGA board
Preliminary
Each laboratory assignment contains a “Preliminary” section that involves tutorials, training, and reading that will help you get started with the lab. You are required to read and attempt to complete the laboratory preliminary before obtaining help from TAs. TAs will not provide help on the laboratory portion of the assignment until you have completed the preliminary section. TAs are available to help you complete the preliminary section if you get stuck but you are encouraged to get as much done on your own as possible.
This preliminary section will guide you through the laboratory submission process and review the Digital and embedded laboratory policies.
Teams Lab Channel
There is a dedicated channel in the class MS Teams workspace for each laboratory assignment. You need to join the Teams workspace for this class if you have not already done so. You can find the link to the Teams workspace by accessing Learning Suite syllabus and opening the “Grading Policy” section. This Teams channel is used to provide updates or clarification on the lab as problems are discovered. Students are encouraged to ask questions about the lab on this channel and provide answers to other students. The TAs and instructor will monitor this channel and provide responses as needed.
What is the preferred way to communicate with the TAs and instructor for laboratory assignments?
Laboratory Completion Instructions
Begin this preliminary by carefully reading through the instructions for completing lab assignments. After reading these instructions, answer each of the following questions in your lab report (i.e., Learning Suite).
What portion of your composite laboratory grade is the “Lab Report” component?
How do you submit a laboratory report in this class?
When are laboratory lab reports due?
Are late lab reports accepted?
How are files submitted for the passoff section of the lab?
When are laboratory Pass Offs due?
Are late lab passoffs accepted?
ECEN Digital and Embedded Labs
Unlike other lab classes, there is not a dedicated lab section for ECEN 423. You will use the computers in room 423 EB (digital lab) and room 438 (embedded lab) to access the software for designing digital hardware. However, you will need to access these labs on your own time. Review the Digital Lab Schedule and the Embedded Lab Schedule to determine when these labs are open. Do not access these labs during closed lab classes.
To access these computers, you will need an active CAEDM account. When in these rooms, you are required to follow all CAEDM policies. You may access these computers remotely by following the instructions found here. Answer the following question:
When are you allowed to access the Digital/Embedded Labs?
Which activities are acceptable in the Digital/Embedded Labs?
The computers in this lab are configured with Linux and you should be familiar with Unix commands to run tools, manage files, and complete laboratory assignments.
GitHub will be used extensively in this class for submitting and grading your laboratory files.
You will be required to create a GitHub classroom repository to store your laboratory files.
Carefully read and follow the instructions in the GitHub Setup Guide to setup your class repository and import the initial class code.
After completing the instructions in this tutorial and creating your GitHub repository, provide the remote GitHub repository string on Learning Suite.
You can obtain the repository by executing the following command within your repository: git remote get-url origin.
Your response should be in the following form: git@github.com:byu-ecen423-classroom/423-labs-wirthlin.git (although you will have a different repository name in the same repository classroom).
This string will be used by the grading scripts to clone your repository.
Provide your class GitHub repository
It is essential that you copy this string correctly. The TA grading scripts will use the string you provide here for extracting your code. You will face a 20% penalty on this lab if this string is entered incorrectly or if the repository is not accessible.
You will need to become familiar with using GitHub for submitting your laboratory files.
To learn some of the most basic functions of Git, complete the GitHub Basic Tutorial.
As part of this tutorial you will create a file named aboutme.txt and commit it to your repository (read the instructions carefully and completely to make sure you include everything).
Make sure the file ‘aboutme.txt’ is committed in the ‘lab01’ directory of your repository.
Note: This green text above indicates that the ‘aboutme.txt’ must be included in your passoff GitHub repository when you submit your lab. This file should contain the information requested during the tutorial and will be reviewed by the TAs.
After reading the instructions on GitHub, answer each of the following questions in your lab report to demonstrate your understanding of Git and its use in the class.
What type of git repository will you be creating for this class?
What git commands should you run to update the starter code in your repository throughout the semester?
Intermediate Files
Many intermediate files will be created as you work through the laboratory assignments.
These intermediate files should not be committed to your repository as they are regenerated every time you change your design and clutter up your file system.
To successfully pass off the lab, you must properly ignore these files in your GitHub repository by them in your .gitignore file.
In addition, you must clean all of these files with the makefile ‘clean’ rule.
The passoff script will check to make sure you are ignoring all intermediate files and that your ‘clean’ rule works properly.
Exercises
Exercise #1 - SystemVerilog, Synthesis, and Implementation Review
Your class repository should contain a directory lab01 that contains a number of files that will be used in this exercise.
Make sure you have access to this directory in your local repository as you will need these files to complete several of the lab exercises.
For this exercise, you will review the SystemVerilog code for a simple button counter circuit.
All the files for simulating, synthesizing, implementing, and submitting this design are included in the buttontcount directory of your local repository.
This directory is a sample “lab” that you will use to learn the laboratory submission process and review your SystemVerilog skills.
Complete the buttoncount tutorial to familiarize yourself with the process of simulating, synthesizing, and implementing a SystemVerilog design on the Basys3 FPGA board.
Make sure to answer all the questions from the tutorial in your laboratory report.
Exercise #2 - Up/Down Button Counter
In this exercise, you will create a new SystemVerilog file that performs both ‘up’ counting and ‘down’ counting (i.e., an up/down counter) using the switches.
You will simulate, synthesize, and implement the design onto the Basys3 board.
Copy the buttoncount.sv file buttoncount tutorial and name it updownbuttoncount.sv.
Modify this file to incorporate a number of changes:
- Add input ports:
btnd,btnl, andbtnrfor the “Down button”, “Left button”, and “Right button”. - Add a 16-bit input port named
swfor the 16 switches on the Basys3 board - Add three instances of the
synchronizerandoneshotmodule to generate a one shot signal for each of the three button inputs (i.e., for btnd, btnl, and btnr). - Modify the counter logic to operate as follows:
- increment the counter by 1 every time ‘btnu’ button is pressed (this is the same functionality as the original buttoncount module).
- decrement the counter by 1 every time ‘btnd’ button is pressed.
- increment the counter by the value indicated on the switches every time ‘btnl’ is pressed
- decrement the counter by the value indicated on the switches every time ‘btnr’ is pressed
In this course you are required to follow a coding standard for all code you generate, including your SystemVerilog code. Review the coding standards as you create your new file. Include the updownbuttoncount.sv in your GitHub repository.
In this lab (and all future labs) you will need to create a makefile that includes a number of predefined rules to simulate, synthesize, and implement your design.
The lab passoff script will run these rules to verify your design.
The actual rules you need to implement will be described below.
Create an empty makefile in your lab01 directory where these rules will be added.
Further, create an empty .gitignore file in your lab01 directory to ignore all intermediate files that are generated during the lab process.
The actual files that must be ignored will be determined when you run the steps described below.
GUI Simulation
After creating your new SystemVerilog file, you will need to simulate it to make sure it is working properly. As with the buttoncount example, you will simulate this interactively using the GUI and with a SystemVerilog testbench.
Create a .tcl simulation file named updownbuttoncount_sim.tcl to simulate your new updownbuttoncount module.
Include commands to demonstrate both up and down counting as well as up and down counting by the switch value.
(Note: there is a coding standard for .tcl files - refer to the coding standard guidelines to make sure you code your .tcl file properly).
Include at least three single up counts, single down counts, switch up counts, and switch down counts.
Include the updownbuttoncount_sim.tcl file in your GitHub repository.
After generating a waveform, take a screenshot of this window and name the file updownbuttoncount_sim.png.
Instructions and requirements for taking screenshots on the digital lab computers can be found here.
Include the updownbuttoncount_sim.png image in your lab01 directory of your lab repository.
Testbench Simulation
After debugging your counter with the GUI simulation, you will need to simulate your design with a testbench to make sure it is working properly.
This testbench, updownbuttoncount_tb.sv, is provided for you in the starter code and is written to test a variety of conditions.
Create a makefile rule named sim_updownbuttoncount_tb that simulates your updownbuttoncount module with the testbench (see the makefile from the buttoncount example as an example of how to do this)
This rule should generate a log file named sim_updownbuttoncount_tb.log that will be reviewed by the passoff script.
After making sure your module passes the testbench, test your simulation and makefile rule by running the passoff command listed below. This command performs one of the steps that will be completed during the passoff process. It will be easier to debug problems with the passoff process by running passoff steps individually than by running all the passoff steps at the same time. Resolve any problems with the passoff testbench before attempting to submit your lab.
python3 passoff.py --run_rule sim_updownbuttoncount_tb
Synthesis
Once your updownbuttoncount module is successfully simulated, you are ready to synthesize your design.
The first step in the synthesis process is to create the .xdc constraints file to define the pinout locations of the top-level design.
Create a .xdc file for your updownbuttoncount design by copying the buttoncount.xdc file and modifying it to include the additional buttons and switches.
You will need to include the .xdc file in your repository for the passoff.
Next, create a synthesis Tcl script to perform synthesis for the updownbuttoncount design (use the synth_buttoncount.tcl file as a guide).
Create a makefile rule named updownbuttoncount_synth.dcp to run this synthesis script.
This rule should generate a synthesis logfile named updownbuttoncount_synth.log as well as the design checkpoint file updownbuttoncount_synth.dcp.
Run your makefile rule to generate the synthesis files and answer the following questions based on your review of the synthesis log file.
To prepare for the passoff, test your synthesis rule by running the following command:
python3 passoff.py --run_rule updownbuttoncount_synth.dcp
Implementation
After successfully synthesizing your design, you will need to implement your design onto the Basys3 FPGA.
Create an implementation Tcl script to perform implementation for the updownbuttoncount design (use the imp_buttoncount.tcl file as a guide).
Next, create a makefile rule named updownbuttoncount.bit to run this implementation script.
This makefile rule should generate the updownbuttoncount.bit bitfile as well as the following log and report files:
updownbuttoncount_imp.logupdownbuttoncount_utilization.rptupdownbuttoncount_timing.rpt
Test your makefile rule manually on the command line. Also, test your makefile rule with the passoff script to resolve any makefile or implementation problems (i.e., make sure you are generating the correct files).
python3 passoff.py --make_rule updownbuttoncount.bit
Indicate the number of resources consumed by your new design in the laboratory report.
Determine the “Worst Negative Slack” or WNS of this circuit.
Download
Once you have successfully generated a bitstream for your new Up/Down button counter, download this bitstream to your Basys3 board. Experiment with your circuit and verify that (1) you can count up, (2) that you can count down, and (3) that you can reset the counter by pressing the center button. The TAs will generate a bitfile and verify that it works correctly so make sure your circuit works correctly to avoid losing points during bitfile grading.
Pass Off
The final step in the laboratory process is to complete the ‘pass off’. Carefully review the instructions for Git Submission as you prepare your submission for this lab. You will need to run the following command successfully to submit your lab:
python3 passoff.py --submit
Answer the final two questions in your laboratory report:
How many hours did you work on the lab?
Provide any suggestions for improving this lab in the future
How did you use AI to help you with this lab